DJI Camera Replacment Gimbal Calibration FIX!!!
How to fix and replace DJI Gimbal. Software Side.
Fix For Phantom 1, Phantom 2, Inspire 1, Phantom 3, Matrice 100, Phantom 3, Agras MG-1, Phantom 3 4K, Phantom 4 , Matrice 600, Mavic Pro, Inspire 2, Phantom 4 Pro, Matrice 200, Agras MG-1S, Phantom 4, Spark, Mavic Air, Phantom 4 Pro V2, Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom, Mavic 2 Enterprise, Mavic 2 Enterprise Dual, Mavic Mini, Mavic Mini 2, Mavic Air 2, (MAVIC) AIR 2S, Gimbal IMU Data error (Code: 40021)
I'm Mainly here to try and Make your life easier. I had Issues with my DJI MINI 2 when I broke the camera gimbal. This will fix all the above DJI Drones
My Story
HOW TO FIX SOFTWARE IMU Calibration Error
What You need:
- DJI Drone (DJI Mini 2 is used in this example)
- PC (Windows 10, Mac, or Linux)
- USB-C Cable or cable compatible with your drone.
- DJI Assistant (Download one that supports your drone)http://fumacrom.com/2CRw9 or https://www.dji.com/uk/downloads/softwares/assistant-dji-2-for-mavic
- Latest Python for your operating system: http://fumacrom.com/2CRwz or https://www.python.org/downloads/ (Windows Version)
- DJI Firmware Tools: http://fumacrom.com/2CRxh or https://github.com/o-gs/dji-firmware-tools/archive/master.zip
- PYserial: Download "tar.gz" File type - http://fumacrom.com/2CRyA or https://pypi.org/project/pyserial/#files
- 7zip: http://fumacrom.com/2CRzG or https://www.7-zip.org/a/7z1900.exe (Any archive tool capable of opening .tar.gz files will work)
- Drone code name a list will be provided. E.g WM240, WM245, WM160
- A level surface for calibration
- Save everything to Desktop to make life EASY
Download and Install Python
Download Python installation linked above. Any latest version of Python 3 should work. I chose to install Python with a ‘Custom Installation’ to C:\DJI\python\ and Add Python to environment variables which allows it be ran by just typing ‘python or py’ in the command line. Having issues installing? carry on reading. Python is easy to run because you just type ‘python’ however I used a short path C:\DJI for all of these extractions so that it is easy to navigate to from the command line which we will be doing shortly.
If you get hit with this Error "How to Fix Python Was Not Found Run Without Arguments to Install From the Microsoft Store Error" then follow the Steps from this video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uBnbVqUmZaQ I followed step 1 which fixed the issue.
Download & Extract pyserial
The pyserial archive is a .tar.gz file. This is a tarball archive (.tar extension) with GNU Zip (.gz extension) which is basically a different type of zip archive that Windows does not natively support. Because of this you will need to use 7zip, which is linked above, or another compatible utility to extract the pyserial files. After installing 7zip or another compatible tool just open the pyserial-3.4.tar.gz file. Because of the way .tar.gz files are archived you will go through a few folder levels before you get to the actual needed content folder. I extracted pyserial to C:\DJI\pyserial
Download & Extract DJI Firmware Tools
I extracted the DJI Firmware Tools folder dji-firmware-tools-master contents using 7zip to C:\DJI\firmware-tools Make sure you review the README.md file to understand what these tools do and how they operate!
Download and install DJI Assistant
Connect your DJI Drone and Find the COM Port
Place your drone on a level surface and make sure it is still on and connected Via USB. There is no need to connect the controller.
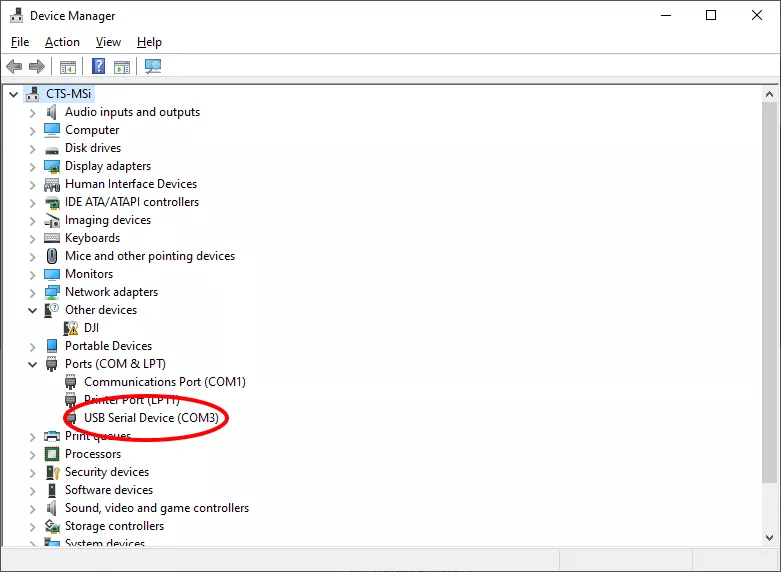
To find the COM port your USB connection is using press the Win+X keys (The ‘Win’ key or Windows Key is usually between Ctrl and Alt on the left side of your keyboard with the Windows logo on it) to open the Power Users menu and select Device Manager. Search for Ports (COM & LPT) section and you should see USB Serial Device (Or Drone name) (COM#). Your COM Number might be different. If there are multiple devices you can disconnect and reconnect the drone to see which device disappears and reappears. Note down the COM port number because you will need it later for running the script.
Install pyserial
Now we need to open an Administrator Command Prompt. Open up (Admin) Command Prompt (CMD) or Windows PowerShell (Admin) and accept the User Account Control warning about making changes to your device.
Once you are in Command Prompt we need to navigate to the pyserial folder we just extracted and install pyserial. to do this use these commands. If you extracted to a different folder you will need to substitute that folder in the commands below.
I.e Copy Folder location
In (Admin CMD) Administrator Command Prompt type "cd " spacebar then paste the file location that you copied with "CTRL + V" . It should look like the image below. Then press enter.
once you pressed enter it should look like this below. Now you're in the folder and we want to
run a program from here using this script " python setup.py install ".
You want to enter in "python setup.py install" and it should look like this... Then
press enter. It should run the code and install the files needed. (I already installed
the files, so no need for me to do again. This part is done.
Calibrate the Gimbal
THE WAIT IS OVER! We need to navigate to the DJI Firmware Tools folder and execute the commands to get our gimbal re-calibrated. Just like how I showed you above "cd " (copy and paste folder location) (the highlighted part is the file location. image shown below).
Once you pressed 'enter' you should see this. This means you are in the folder and are ready to run the code
- A2 = 0 # Released 2013-09-04 A2 Flight Controller
- P330 = 1 # Released 2013-01-07 Phantom 1
- P330V = 2 # Released 2013-10-28 Phantom 2 Vision
- P330Z = 3 # Released 2013-12-15 Phantom 2 w/ Zenmuse H3-2D
- P330VP = 4 # Released 2014-04-07 Phantom 2 Vision+
- WM610 = 5 # Released 2014-11-13 Inspire 1
- P3X = 6 # Released 2015-03-09 Phantom 3 Professional
- P3S = 7 # Released 2015-03-09 Phantom 3 Advanced
- MAT100 = 8 # Released 2015-06-08 Matrice 100
- P3C = 9 # Released 2015-08-04 Phantom 3 Standard
- MG1 = 10 # Released 2015-11-27 Agras MG-1
- WM325 = 11 # Released 2016-01-05 Phantom 3 4K
- WM330 = 12 # Released 2016-03-02 Phantom 4
- MAT600 = 13 # Released 2016-04-17 Matrice 600
- WM220 = 14 # Released 2016-09-28 Mavic Pro
- WM620 = 15 # Released 2016-11-16 Inspire 2
- WM331 = 16 # Released 2016-11-16 Phantom 4 Pro
- MAT200 = 17 # Released 2017-02-26 Matrice 200
- MG1S = 18 # Released 2017-03-28 Agras MG-1S
- WM332 = 19 # Released 2017-04-13 Phantom 4 Advanced
- WM100 = 20 # Released 2017-05-24 Spark
- WM230 = 21 # Released 2018-01-23 Mavic Air
- WM335 = 22 # Released 2018-05-08 Phantom 4 Pro V2
- WM240 = 23 # Released 2018-08-23 Mavic 2 Pro/Zoom
- WM245 = 24 # Released 2018-10-29 Mavic 2 Enterprise
- WM246 = 25 # Released 2018-12-20 Mavic 2 Enterprise Dual
- WM160 = 26 # Released 2019-10-30 Mavic Mini <<< DJI MINI 2 I have tried and tested myself (they use the same controller)
- WM231 = 27 # Released 2020-04-28 Mavic Air 2
- WM232 = 28 # Released 2021-04-15 (MAVIC) AIR 2S
now enter This code below into the CMD terminal. (you can copy this code into a notepad and change it)
python comm_og_service_tool.py com3 WM160 GimbalCalib JointCoarse
^ ^
Change these according to your COM# number and Drone model. VERY IMPORTANT!^ ^
Change these according to your COM# number and Drone model. VERY IMPORTANT!Test & Fly
Hopefully your calibration was successful. Disconnect the Micro USB and connect your remote along with your phone or tablet. Your picture should now be level. I attempted some motions with the drone in my hand and everything looked good. Next I preformed my pre-flight check and took it up for a quick test flight to verify everything was working as it should and let out a big sigh of relief.